Core Nutritionals POISE
$44.49
- Magnesium and Iodine: Provides optimal thyroid hormone balance. Aids in menstrual symptom relief.
- Chaste Tree Extract – Can provide menstrual symptom relief.
- Setria® Glutathione – Antioxidant rich. Neutralizes free radicals.
- BioPerine® – Increased bioavailability of key nutrients.
- ✔ Percentage Reward Add this item to unlock your discount to get 30% off !
In stock
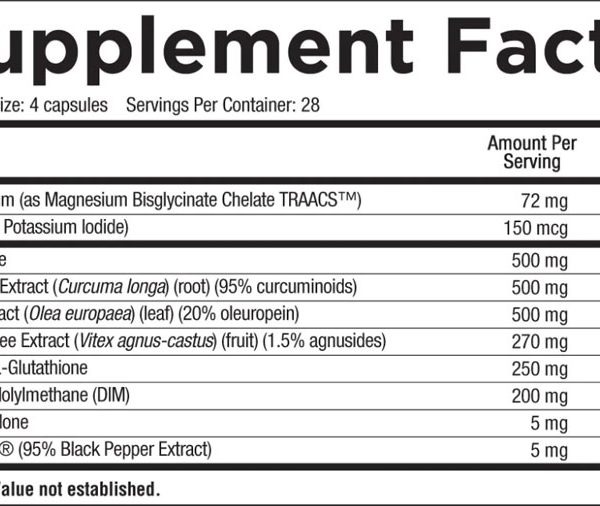
Magnesium (as Magnesium Bisglycinate Chelate (TRAACS™):
It is difficult to overstate the biological necessity of magnesium. Magnesium is a co-factor in over 300 enzymatic reactions that regulate essential physiological functions such as protein synthesis, glucose homeostasis, muscle and nerve function, and the maintenance and support of healthy blood pressure levels.
In addition to these benefits, magnesium (especially Magnesium Bisglycinate Chelate) has been studied for its benefits in reducing dysmenorrhea (menstrual cramps) through its ability to relax the smooth muscle of the uterus and reduce the prostaglandins that cause painful cramps. Magnesium levels also tend to fluctuate during a menstrual cycle. During the second half of a cycle when estrogen and progesterone are higher, magnesium levels tend to drop even more. Supplementation with a high-quality magnesium can assist in maintaining an optimal level.
Magnesium’s influence on the thyroid is also of importance. Magnesium is responsible not only for making the inactive T4 (thyroxine) in the thyroid gland but also for converting T4 into the active form of T3 (triiodothyronine). This is important because the metabolism of your body’s cells is enhanced by T3 specifically. These two hormones have a large influence on metabolic rate, heart and digestive function, muscle control, brain development and bone maintenance. Studies have shown that severely low serum magnesium can be associated with an increased risk of anti-thyroglobulin antibodies, which can be a sign of thyroid gland damage caused by the immune system. It has also shown an increased risk of Hashimoto thyroiditis and hypothyroidism, two common autoimmune disorders.
Iodine:
Iodine is a trace element naturally present in certain foods, including kelp. Iodine is a critical component for fetal development, especially during early pregnancy, as maternal T4 (thyroxine) is the sole source of fetal thyroid hormone. After birth, especially if breast-feeding, iodine remains an important constituent of a balanced-diet to maintain adequate T3 (triiodothyronine) and T4 (thyroxine) levels in the mother and for proper cognitive development in the child.
As implied, however, the most important of iodine’s functions is assisting the body’s production and maintenance of both thyroid hormones and TSH (thyroid stimulating hormone, released by the pituitary). The thyroid hormones, in turn, regulate several critical biochemical reactions, including protein synthesis, and, along with norepinephrine/epinephrine, largely determine the body’s metabolic rate.
In addition to these benefits for the thyroid, iodine can also be a critical element for women’s health. About 70% of the body’s iodine is concentrated in the tissues of the brain, immune system, ovaries, uterus, breasts, and prostate gland (in men). Being this close to the female reproductive system, iodine also has a large effect on ovulation and estrogen. Iodine is believed to reduce ovulation pain, prevent ovarian cysts, and boost progesterone levels when there is too much estrogen present, which can cause heavy menstruation, breast pain, fibroids, and premenstrual irritability. Iodine can also help reduce estrogen related side effects in two ways: by promoting healthy detoxification of estrogen and by making cells less sensitive to estrogen.
L-Tyrosine:
Tyrosine is amongst a class of amino acids known as ‘non-essential’ amino acids, so called because the body can produce them endogenously, and it is therefore not essential through dietary means. That being said, tyrosine is also what is known as a conditionally-essential amino acid; conditionally-essential because, along with glucose and ammonia, the synthesis of tyrosine additionally requires adequate levels of phenylalanine. Once synthesized, tyrosine is one of the most critical amino acids, given its prominent role as a substrate in the synthesis of the catecholamines dopamine, norepinephrine, and epinephrine, in addition to both T3 (triiodothyronine) and T4 (thyroxine) thyroid hormones.
Thyroid hormones are in fact derivatives of tyrosine that are bound covalently to iodine, meaning that tyrosine (as well as iodine) needs to be present in order for thyroid hormones to be produced. This supplementation can boost thyroid hormones levels in those who may have suppressed thyroid hormones levels. (It is important to note, however, that individuals who are already being prescribed thyroid medications or have an overactive thyroid should be cautious when supplementing with tyrosine and should seek the guidance of a healthcare professional prior to supplementing).
Turmeric Extract (Curcuma longa) (root) (95% curcuminoids):
Curcumin, the primary curcuminoid found in turmeric (a root known for its spice), has been the basis of many clinical studies for its therapeutic properties and ability to modulate multiple cells signaling pathways in certain inflammatory diseases known to humans.
Numerous studies seem to suggest that curcumin powerfully inhibits the enzymes that synthesize inflammatory compounds such as prostaglandins and leukotrienes. In particular, basic research and molecular studies have now firmly established curcumin’s ability to dose-dependently and potently inhibit a transcription factor known as NF–kB – a molecule involved in the proliferation of pro-inflammatory cytokines, soft tissue destruction, and autoimmune responses. In relation to autoimmune conditions, Hashimoto’s thyroiditis is one in particular that is considered the leading cause of hypothyroidism. The overabundance of chronic inflammation found in the thyroid during these conditions can lead to less production of thyroid hormone all together, thus leading to a generalized slowing of a person’s metabolism.
Turmeric can also have a positive impact on PMS related symptoms. This is seen primarily through the increased neurotransmitter release and inflammatory response associated with pre-menstrual occurrences. Many of the mood and behavior changes associated with PMS can be traced to neurotransmitter changes such as decreased norepinephrine, dopamine, and serotonin. These changes can be subject to the decline in estrogen and progesterone during this period. Turmeric has been shown in studies to increase these neurotransmitters, thus impacting these symptoms in a positive way. The increased inflammatory response due to the PMS period as well can be mitigated in the presence of turmeric due to its high anti-inflammatory benefits.
Studies have shown that low quality curcumin has low bioavailability and benefit, which is why we have used a high standard curcumin with 95% curcuminoids and have also included the trademarked Bioperine® in this formula. These two ingredients have a largely cohesive impact that can drastically improve the health benefit. Studies have shown that Bioperine® significantly improved curcumin uptake by upwards of 2000% at doses that proved to be clinically beneficial.
Olive Extract (Olea europaea) (leaf) (20% Oleuropein):
Using products derived from the olive tree for the basis of benefitting human health dates back several centuries. There has been a good body of research done lately on the benefits of olives and its derivatives. The polyphenols found in olives (and unrefined virgin olive oil) contain highly potent antioxidant and free radical fighting properties, making them highly sought out for their anti-inflammatory and immune boosting benefits. As we have discussed in subsequent ingredients and their benefits, these anti-inflammatory and immune boosting benefits include the positive impacts made towards thyroid health and PMS. Oleuropein is the most potent polyphenol found in olives (our source of olives contains 20%) and exhibits a very high antioxidant effect on the body through different mechanisms, resulting in an enhanced antioxidant response. This potential is mainly related to its ability to improve radical stability through the formation of intramolecular hydrogen bonds. Oleuropein may also be able to counteract oxidative stress and has shown in vitro to have a protective effect on lipid oxidation. As mentioned above, olive-derived phenolic compounds, including oleuropein, can have a beneficial anti-inflammatory effect. These compounds can decrease concentrations of pro-inflammatory agents that stimulate more inflammation in several different pathologies. It has been studied that oleuropein is able to elicit protective effects on modulating parameters of inflammation and other oxidative stressors.
Oleuropein has also been seen is studies to have positive impacts on thyroid conditions, in particular hypothyroidism (underactive thyroid), where the thyroid underproduces thyroxine and and overproduces Thyroid Stimulating Hormone (TSH). This high level of TSH can be expressed from the pituitary gland secreting excess amounts of TSH to stimulate the thyroid gland to produce more thyroid hormone in an attempt to balance secretions. Olive leaf supplementation has been shown to positively impact the thyroid this by promoting a lowering of TSH levels and increasing T3 (triiodothyronine) levels in an attempt to normalize thyroid function.
Chaste Tree Extract (Vitex agnus-castus) (fruit) (1.5% Agnusides)
Chaste Tree Berry, also known as Vitex agnus castus (VAC), is a shrub that is native to both Mediterranean Europe and Central Asia. Clinical reviews have supported the use of VAC as a remedy for many female conditions, including menstrual disorders (amenorrhea, dysmenorrhea), premenstrual syndrome (PMS), corpus luteum insufficiency, hyperprolactinemia, infertility, acne, menopause, and disrupted lactation. Chaste Berry exhibits a mechanism of action that increases dopamine activity in the brain, which results in a reduction of prolactin release in the body. When there is an increase in prolactin it can cause disturbances in a women’s menstrual cycle as well as deficiency in their levels of estrogen and progesterone. A prospective, multicenter trial in the efficacy of VAC on PMS was investigated in 50 patients. The Moos’ menstrual distress questionnaire (MMDQ) was the primary parameter and self-assessment was the second parameter. The inclusion of VAC showed that PMS-related symptoms were reduced but then gradually returned after cessation of the trial period. Studies such as this one show that using VAC as a remedy for the symptoms associated with PMS can show clear improvements but should mainly be used for symptomatic relief rather than relief for the duration of the syndrome.
Setria® L-Glutathione:
PMS is often a high stress event for an individual. The overabundance of estrogen compared to progesterone can increase overall stress. When cortisol is not controlled, it can further lower progesterone, further dividing the needed balance between these two complimentary hormones. Glutathione is an amino acid containing molecule of L-glutamic acid, L-cysteine, and Glycine. It is vital to many different properties and is best known for being a powerful antioxidant. The ‘glutathione system’ comprises the enzymes that synthesize glutathione within a cell as dedicated enzymes that use glutathione for its antioxidant effects. Glutathione supplementation is thought to support this pool of glutathione present in cells and thus maintain the efficacy of the entire system. Free radicals can be a byproduct of many different things such as exercising, eating, and breathing to name a few. When these molecules overcome the body at the cellular level, this constant barrage can have negative impacts on health and overall wellness. This barrage can also include the stresses that one’s body might endure during pre-menstruation. Setria® L-Glutathione provides a potent supply of antioxidants that bind these free radicals, which can help keep them from causing lasting damage. Glutathione not only has the ability to neutralize free radicals, but it also can reactivate other antioxidants, such as Vitamin C and Vitamin E. Once these vitamins and their antioxidants do their job of neutralizing free radicals, they become unstable radicals themselves. Glutathione can help recycle these unstable molecules back to their antioxidant rich properties.
3,3′-Diindolylmethane (DIM):
What we typically refer to as “Estrogen,” is in fact a group of three biologically distinct hormones – estradiol (E2), estrone (E1), and estriol (E3), each possessing different activities in different cell, tissue, and receptor types. When experts refer to either the benefits or downfalls of “estrogen,” they really mean to (but probably cannot) identify a specific estrogen.
These specific estrogens, in turn, metabolize into even more specific estrogen sub-compounds, such as the 2-hydroxyestrogens (2-OHE’s), 2-methoxyestrogens, 16a-hydroxyestrone (16-OHE1), and 4-hydroxyestrogens (4-OHE’s). As their parent estrogens, these estrogen metabolites exert different effects depending upon the tissue and cell one is examining. In fact, two estrogen metabolites in particular, 16-OHE1 and 2-OHE, have such contrasting cellular activities that 2-OHE is an estrogen antagonist. Yes, that is correct: there is an anti-estrogen, estrogen.
In recent years, so-called “phytonutrients” have become the focus of clinical research, as these natural compounds have shown the ability to increase the ratio of good, estrogen decreasing estrogens (such as 2-OHE), to bad, estrogen increasing estrogens (such as 16-OHE1). One of these phytonutrients, a dietary indole known as indole-3-carbinol (I3C), is the bioactive phytochemical and a presumed modulator of reduced cancer risk in areas with high cruciferous vegetable consumption. Unfortunately, despite its potent antiestrogenic activity, I3C is highly molecularly unstable, and therefore unsuitable for use as a therapeutic agent or dietary supplement.
Luckily, however, I3C readily metabolizes into the secondary indole 3,3’ diindolylmethane, or DIM for short. When used in a supplemental fashion in clinical trials, DIM appears to possess all the positive effects of its parent compound with respect to antiestrogenic action – promoting the metabolism of beneficial estrogens that themselves reduce estrogenic activity.
Aside from its healthy-estrogen promoting abilities, DIM also exerts its own direct physiological effects, including:
- Promoting pathways of internal estrogen metabolism that favor the production of anti-estrogen estrogens.
- Adjusting the activity of certain cytochrome enzymes, reducing the activity at the estrogen receptor site.
- Limit the cell division and growth of certain estrogens.
Despite the bodybuilding community’s single-minded crusade to eliminate estrogen wherever it lie in wait, compounds such as DIM show us that estrogen is a very diverse set of compounds – and that we should actively pursue increasing certain estrogens that have beneficial, and ironically, anti-estrogenic effects
Pregnenolone:
Pregnenolone, or pregn-5-en-3β-ol-20-one, is known as the grandmother hormone due to its precursor role in the endogenous biosynthesis of most steroid hormones as well as others, including progesterone and estrogen. Pregnenolone also has a high relationship in the balancing of beta-estradiol and progesterone, which can have a positive impact on the distressing of symptoms associated with PMS, including menopausal depression. When pregnenolone levels are low, whether it be due to high amounts of oxidative stress, increased cortisol, etc. it can have a negative impact on other bodily functions that are governed by hormones. When women in particular have low progesterone during their monthly cycle, it can lead to heavy menstruation and increased levels of estrogen, which can decrease sex drive and increase weight gain. Pregnenolone needs to be present in order for the balance of progesterone and estrogen to occur. This balance of hormones can thus lead to more balance during the menstruation period and lower the severity of PMS symptoms.
Bioperine® (95% Black Pepper Extract):
BioPerine® is a patented standardized extract from the fruit of Piper nigrum (black pepper). It’s studied benefits have shown improvements in bioavailability of nutrients it is surrounded by. In this specific product for Core POISE, it is included because it dramatically increases the bioavailability of curcuminoids (see above). Without Bioperine, the serum concentration and absorption rates of the active agents in curcumin would be significantly reduced.
BioPerine® primarily works through mechanisms and channels that can inhibit intestinal motility and dilate blood vessels of the intestines (where absorption of nutrients occurs). This physiological action may cause increased absorption and digestion of nutrients.
Several studies looking at the impact of BioPerine® on nutrient absorption have been done. One study looking at the efficacy of BioPerine® on serum concentrations of curcumin showed bioavailability was improved by more than 500%. Therapeutic effectiveness of curcumin has often been exhibited as low. Another study conducted over the course of 6 weeks on BioPerine® influence on serum selenium levels in humans showed an increase by 145% over the presupplementation value.
With promising research being done on the effects of BioPerine® in the context of nutrient absorption and bioavailability, it is only fitting that we include it in Core POISE.
Related products
General Health
Amino Acids
General Health
General Health
General Health
General Health
General Health
General Health
General Health
General Health
General Health
General Health
General Health
Diuretics
General Health
General Health
General Health
General Health
General Health
General Health
General Health
General Health
General Health
General Health
General Health